Preprocessing dMRI data
Overview
Teaching: 30 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
What are the standard preprocessing steps?
How do we register with an anatomical image?
Objectives
Understand the common preprocessing steps
Learn to register diffusion data
Diffusion Preprocessing
Diffusion preprocessing typically comprises of a series of steps, which may
vary depending on how the data is acquired. Some consensus has been reached for
certain preprocessing steps, while others are still up for debate. The lesson
will primarily focus on the preprocessing steps where consensus has been
reached. Preprocessing is performed using a few well-known software packages
(e.g. FSL, ANTs). For the purposes of these lessons, preprocessing steps
requiring these software packages has already been performed for the dataset
ds000221 and the commands required for each step will be provided.
This dataset contains single shell diffusion data with 7 volumes
(non-diffusion weighted) and 60 volumes. In addition, field
maps (found in the fmap directory are acquired with opposite
phase-encoding directions).
To illustrate what the preprocessing step may look like, here is an example
preprocessing workflow from QSIPrep (Cieslak et al, 2020):
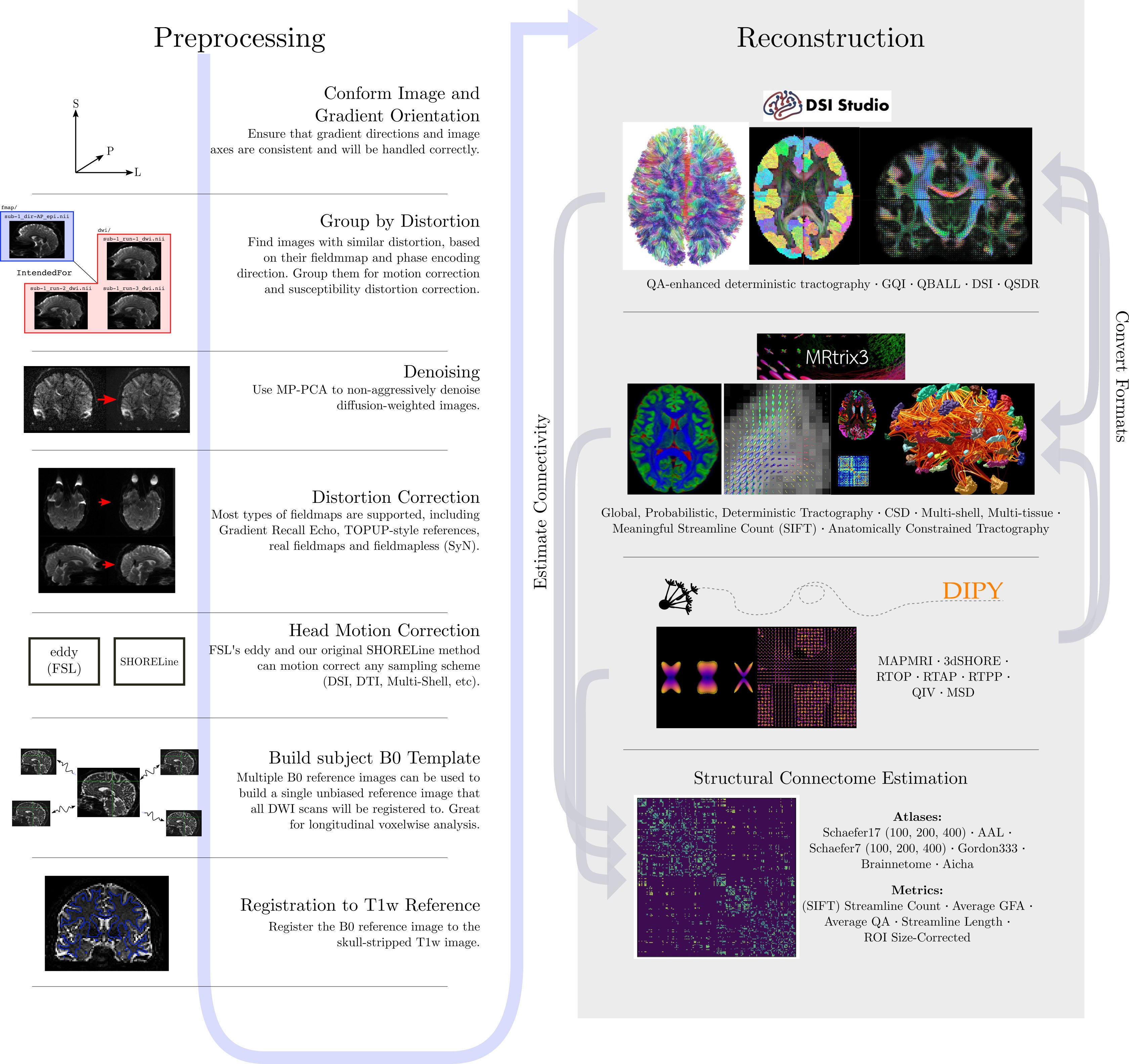
dMRI has some similar challenges to fMRI preprocessing, as well as some unique ones.
Our preprocesssing of this data will consist of following steps:
- Brainmasking the diffusion data.
- Applying
FSLtopupto correct for susceptibility induced distortions. FSLEddy current distortion correction.- Registration to T1w.
The same subject (sub-010006) will be used throughout the remainder of the
lesson.
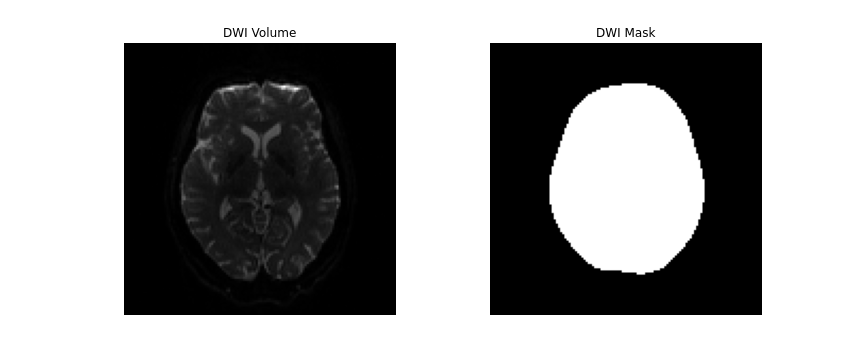
Brainmasking
The first step to the preprocessing workflow is to create an appropriate brainmask from the diffusion data! Start, by first importing the necessary modules. and reading the diffusion data! We will also grab the anatomical T1w image to use later on, as well as the second inversion from the anatomical acquisition for brainmasking purposes.
from bids.layout import BIDSLayout
layout = BIDSLayout("../../data/ds000221", validate=False)
subj='010006'
# Diffusion data
dwi = layout.get(subject=subj, suffix='dwi', extension='.nii.gz', return_type='file')[0]
# Anatomical data
t1w = layout.get(subject=subj, suffix='T1w', extension='.nii.gz', return_type='file')[0]
import numpy as np
import nibabel as nib
dwi = nib.load(dwi)
dwi_affine = dwi.affine
dwi_data = dwi.get_fdata()
DIPY’s segment.mask module will be used to create a brainmask
from this. This module contains a function median_otsu, which can
be used to segment the brain and provide a binary brainmask! Here, a brainmask
will be created using the first non-diffusion volume of the data. We will save
this brainmask to be used in our later future preprocessing steps. After
creating the brainmask, we will start to correct for distortions in our images.
import os
from dipy.segment.mask import median_otsu
# vol_idx is a 1D-array containing the index of the first b0
dwi_brain, dwi_mask = median_otsu(dwi_data, vol_idx=[0])
# Create necessary folders to save mask
out_dir = f'../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected/sub-{subj}/ses-01/dwi/'
# Check to see if directory exists, if not create one
if not os.path.exists(out_dir):
os.makedirs(out_dir)
img = nib.Nifti1Image(dwi_mask.astype(np.float32), dwi_affine)
nib.save(img, os.path.join(out_dir, f"sub-{subj}_ses-01_brainmask.nii.gz"))
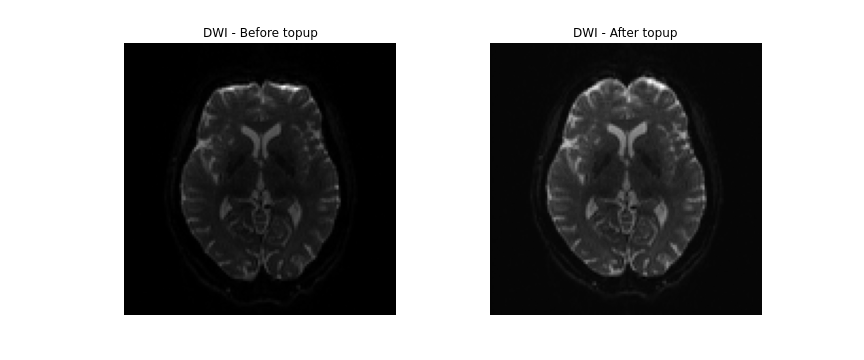
FSL topup
Diffusion images, typically acquired using spin-echo echo planar imaging (EPI), are sensitive to non-zero off-resonance fields. One source of these fields is from the susceptibilitiy distribution of the subjects head, otherwise known as susceptibility-induced off-resonance field. This field is approximately constant for all acquired diffusion images. As such, for a set of diffusion volumes, the susceptibility-induced field will be consistent throughout. This is mainly a problem due to geometric mismatches with the anatomical images (e.g. T1w), which are typically unaffected by such distortions.
topup, part of the FSL library, estimates and attempts to
correct the susceptibility-induced off-resonance field by using 2 (or more)
acquisitions, where the acquisition parameters differ such that the distortion
differs. Typically, this is done using two acquisitions acquired with opposite
phase-encoding directions, which results in the same field creating distortions
in opposing directions.
Here, we will make use of the two opposite phase-encoded acquisitions found in
the fmap directory of each subject. These are acquired with a
diffusion weighting of . Alternatively, if these are not
available, one can also extract and make use of the non-diffusion weighted
images (assuming the data is also acquired with opposite phase encoding
directions).
First, we will merge the two files so that all of the volumes are in 1 file.
mkdir -p ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/work
fslmerge -t ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/work/sub-010006_ses-01_acq-SEfmapDWI_epi.nii.gz ../../data/ds000221/sub-010006/ses-01/fmap/sub-010006_ses-01_acq-SEfmapDWI_dir-AP_epi.nii.gz ../../data/ds000221/sub-010006/ses-01/fmap/sub-010006_ses-01_acq-SEfmapDWI_dir-PA_epi.nii.gz
Another file we will need to create is a text file containing the information
about how the volumes were acquired. Each line in this file will pertain to a
single volume in the merged file. The first 3 values of each line refers to the
acquisition direction, typically along the y-axis (or anterior-posterior). The
final value is the total readout time (from center of first echo to center of
final echo), which can be determined from values contained within the
associated JSON metadata file (named “JSON sidecar file” within the BIDS
specification). Each line will look similar to [x y z TotalReadoutTime].
In this case, the file, which we created, is contained within the
pedir.txt file in the derivative directory.
0 1 0 0.04914
0 1 0 0.04914
0 1 0 0.04914
0 -1 0 0.04914
0 -1 0 0.04914
0 -1 0 0.04914
With these two inputs, the next step is to make the call to topup
to estimate the susceptibility-induced field. Within the call, a few parameters
are used. Briefly:
--imainspecifies the previously merged volume.--datainspecifies the text file containing the information regarding the acquisition.--config=b02b0.cnfmakes use of a predefined config file. supplied withtopup, which contains parameters useful to registering with good images.--outdefines the output files containing the spline. coefficients for the induced field, as well as subject movement parameters.
topup --imain=../../data/ds000221/derivatives/topup/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/work/sub-010006_ses-01_acq-SEfmapDWI_epi.nii.gz --datain=../../data/ds000221/derivatives/topup/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/work/pedir.txt --config=b02b0.cnf --out=../../data/ds000221/derivatives/topup/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/work/topup
Next, we can apply the correction to the entire diffusion weighted volume by
using applytopup Similar to topup, a few parameters
are used. Briefly:
--imainspecifies the input diffusion weighted volume.--datainagain specifies the text file containing information regarding the acquisition - same file previously used.--inindexspecifies the index (comma separated list) of the input image to be corrected.--topupname of field/movements (from previous topup step.--outbasename for the corrected output image.--method(optional) jacobian modulation (jac) or least-squares resampling (lsr).
applytopup --imain=../../data/ds000221/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/sub-010006_ses-01_dwi.nii.gz --datain=../../data/ds000221/derivatives/topup/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/work/pedir.txt --inindex=1 --topup=../../data/ds000221/derivatives/topup/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/work/topup --out=../../data/ds000221/derivatives/topup/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/dwi --method=jac
FSL Eddy
Another source of the non-zero off resonance fields is caused by the rapid switching of diffusion weighting gradients, otherwise known as eddy current-induced off-resonance fields. Additionally, the subject is likely to move during the diffusion protocol, which may be lengthy.
eddy, also part of the FSL library, attempts to correct for both
eddy current-induced fields and subject movement by reading the gradient table
and estimating the distortion volume by volume. This tool is also able to
optionally detect and replace outlier slices.
Here, we will demonstrate the application of eddy following the
topup correction step, by making use of both the uncorrected
diffusion data, as well as estimated warpfield from the topup. Additionally,
a text file, which maps each of the volumes to one of the corresponding
acquisition directions from the pedir.txt file will have to be
created. Finally, similar to topup, there are also a number of
input parameters which have to be specified:
--imainspecifies the undistorted diffusion weighted volume.--maskspecifies the brainmask for the undistorted diffusion weighted volume.--acqpspecifies the the text file containing information regarding the acquisition that was previously used intopup.--indexis the text file which maps each diffusion volume to the corresponding acquisition direction.--bvecsspecifies the bvec file to the undistorted dwi.--bvalssimilarily specifies the bval file to the undistorted dwi.--topupspecifies the directory and distortion correction files previously estimated bytopup.--outspecifies the prefix of the output files following eddy correction.--repolis a flag, which specifies replacement of outliers.
mkdir -p ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup_eddy/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/work
# Create an index file mapping the 67 volumes in 4D dwi volume to the pedir.txt file
indx=""
for i in `seq 1 67`; do
indx="$indx 1"
done
echo $indx > ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup_eddy/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/work/index.txt
eddy --imain=../../data/ds000221/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/sub-010006_ses-01_dwi.nii.gz --mask=../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/sub-010006_ses-01_brainmask.nii.gz --acqp=../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/work/pedir.txt --index=../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup_eddy/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/work/index.txt --bvecs=../../data/ds000221/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/sub-010006_ses-01_dwi.bvec --bvals=../../data/ds000221/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/sub-010006_ses-01_dwi.bval --topup=../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/work/topup --out=../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup_eddy/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/dwi --repol
Registration with T1w
The final step to our diffusion processing is registration to an anatomical image (e.g. T1-weighted). This is important because the diffusion data, typically acquired using echo planar imaging or EPI, enables faster acquisitions at the cost of lower resolution and introduction of distortions (as seen above). Registration with the anatomical image not only helps to correct for some distortions, it also provides us with a higher resolution, anatomical reference.
First, we will create a brainmask of the anatomical image using the anatomical
acquisition (e.g. T1-weighted). To do this, we will use FSL bet
twice. The first call to bet will create a general skullstripped
brain. Upon inspection, we can note that there is still some residual areas of
the image which were included in the first pass. Calling bet a
second time, we get a better outline of the brain and brainmask, which we can
use for further processing.
mkdir -p ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected/sub-010006/ses-01/anat
bet ../../data/ds000221/sub-010006/ses-01/anat/sub-010006_ses-01_inv-2_mp2rage.nii.gz ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected/sub-010006/ses-01/anat/sub-010006_ses-01_space-T1w_broadbrain -f 0.6
bet ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected/sub-010006/ses-01/anat/sub-010006_ses-01_space-T1w_broadbrain ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected/sub-010006/ses-01/anat/sub-010006_ses-01_space-T1w_brain -f 0.4 -m
mv ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected/sub-010006/ses-01/anat/sub-010006_ses-01_space-T1w_brain_mask.nii.gz ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected/sub-010006/ses-01/anat/sub-010006_ses-01_space-T1w_brainmask.nii.gz
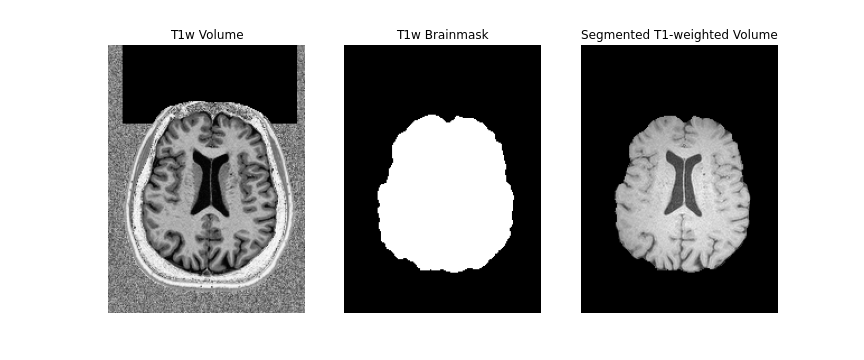
Note, we use bet here, as well as the second inversion of the
anatomical image, as it provides us with a better brainmask. The
bet command above is called to output only the binary mask and the
fractional intensity threshold is also increased slightly (to 0.6) provide a
smaller outline of the brain initially, and then decreased (to 0.4) to provide
a larger outline. The flag -m indicates to the tool to create a
brainmask in addition to outputting the extracted brain volume. Both the mask
and brain volume will be used in our registration step.
Before we get to the registration, we will also update our DWI brainmask by
performing a brain extraction using DIPY on the eddy corrected image. Note
that the output of eddy is not in BIDS format so we will include
the path to the diffusion data manually. We will save both the brainmask and
the extracted brain volume. Additionally, we will save a separate volume of
only the first B0 to use for the registration.
from dipy.segment.mask import median_otsu
# Path of FSL eddy-corrected dwi
dwi = "../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup_eddy/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/dwi.nii.gz"
# Load eddy-corrected diffusion data
dwi = nib.load(dwi)
dwi_affine = dwi.affine
dwi_data = dwi.get_fdata()
dwi_brain, dwi_mask = median_otsu(dwi_data, vol_idx=[0])
dwi_b0 = dwi_brain[:,:,:,0]
# Output directory
out_dir="../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup_eddy/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi"
# Save diffusion mask
img = nib.Nifti1Image(dwi_mask.astype(np.float32), dwi_affine)
nib.save(img, os.path.join(out_dir, "sub-010006_ses-01_dwi_proc-eddy_brainmask.nii.gz"))
# Save 4D diffusion volume
img = nib.Nifti1Image(dwi_brain, dwi_affine)
nib.save(img, os.path.join(out_dir, "sub-010006_ses-01_dwi_proc-eddy_brain.nii.gz"))
# Save b0 volume
img = nib.Nifti1Image(dwi_b0, dwi_affine)
nib.save(img, os.path.join(out_dir, "sub-010006_ses-01_dwi_proc-eddy_b0.nii.gz"))
To perform the registration between the diffusion volumes and T1w, we will make
use of ANTs, specifically the antsRegistrationSyNQuick.sh script
and antsApplyTransform. We will begin by registering the diffusion
volume to get the appropriate transforms to align the two
images. We will then apply the inverse transformation to the T1w volume such
that it is aligned to the diffusion volume.
Here, we will constrain antsRegistrationSyNQuick.sh to perform a
rigid and affine transformation (we will explain why in the final step). There
are a few parameters that must be set:
-d- Image dimension (2/3D).-t- Transformation type (aperforms only rigid + affine transformation).-f- Fixed image (anatomical T1w).-m- Moving image (B0 DWI volume).-o- Output prefix (prefix to be appended to output files).
mkdir -p ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup_eddy_regT1/sub-010006/ses-01/transforms
# Perform registration between b0 and T1w
antsRegistrationSyNQuick.sh -d 3 -t a -f ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected/sub-010006/ses-01/anat/sub-010006_ses-01_space-T1w_brain.nii.gz -m ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup_eddy/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/sub-010006_ses-01_dwi_proc-eddy_b0.nii.gz -o ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup_eddy_regT1/sub-010006/ses-01/transform/dwi_to_t1_
The transformation file should be created which we will use to apply the
inverse transform with antsApplyTransform to the T1w volume.
Similar to the previous command, there are few parameters that will need to be
set:
-d- Image dimension (2/3/4D).-i- Input volume to be transformed (T1w).-r- Reference volume (B0 DWI volume).-t- Transformation file (can be called more than once).-o- Output volume in the transformed space.
Note that if more than 1 transformation file is provided, the order in which the transforms are applied to the volume is in reverse order of how it is inputted (e.g. last transform gets applied first).
# Apply transform to 4D DWI volume
antsApplyTransforms -d 3 -i ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected/sub-010006/ses-01/anat/sub-010006_ses-01_space-T1w_brain.nii.gz -r ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup_eddy/sub-010006/ses-01/dwi/sub-010006_ses-01_dwi_proc-eddy_b0.nii.gz -t [../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup_eddy_regT1/sub-010006/ses-01/transform/dwi_to_t1_0GenericAffine.mat,1] -o ../../data/ds000221/derivatives/uncorrected_topup_eddy_regT1/sub-010006/ses-01/anat/sub-010006_ses-01_space-dwi_T1w_brain.nii.gz
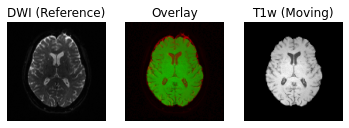
Following the transformation of the T1w volume, we can see that anatomical and diffusion weighted volumes are now aligned. It should be highlighted that as part of the transformation step, the T1w volume is resampled based on the voxel size of the reference volume (i.e. the B0 DWI volume in this case).
Preprocessing notes:
- In this lesson, the T1w volume is registered to the DWI volume. This method
minimizes the manipulation of the diffusion data. It is also possible to
register the DWI volume to the T1w volume and would require the associated
diffusion gradient vectors (bvec) to also be similarly rotated. If this step is
not performed, one would have incorrect diffusion gradient directions relative
to the registered DWI volumes. This also highlights a reason behind not
performing a non-linear transformation for registration, as each individual
diffusion gradient direction would also have to be subsequently warped.
Rotation of the diffusion gradient vectors can be done by applying the affine
transformation to each row of the file. Luckily, there are existing scripts
that can do this. One such Python script was created by Michael Paquette:
rot_bvecs_ants.py. - We have only demonstrated the preprocessing steps where there is general consensus on how DWI data should be processed. There are also additional steps with certain caveats, which include denoising, unringing (to remove/minimize effects of Gibbs ringing artifacts), and gradient non-linearity correction (to unwarp distortions caused by gradient-field inhomogeneities using a vendor acquired gradient coefficient file).
- Depending on how the data is acquired, certain steps may not be possible.
For example, if the data is not acquired in two directions,
topupmay not be possible (in this situation, distortion correction may be better handled by registering with a T1w anatomical image directly. - There are also a number of tools available for preprocessing. In this
lesson, we demonstrate some of the more commonly used tools alongside
DIPY.
References
.. [Cieslak2020] M. Cieslak, PA. Cook, X. He, F-C. Yeh, T. Dhollander, et al, “QSIPrep: An integrative platform for preprocessing and reconstructing diffusion MRI”, https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.04.282269
Key Points
Many different preprocessing pipelines, dependent on how data is acquired